Posted by Sean Corrigan on Wed, Oct 25, 2023 @ 4:40 AM
How to Stop Pavement Lift from Tree Roots

Table of Contents
In urban and suburban settings, trees can provide shade and beauty, but their roots often pose a significant threat to pavements, causing unsightly and hazardous uplifts. This guide explores effective strategies to prevent and address pavement lift from tree roots. Learn how to protect your hardscape, ensure safety, and maintain curb appeal while ensuring your trees are an actual benefit to your urban space.
Related: Top Products for Tree Root Management
What is Pavement Lift?
Pavement lift refers to the situation where sections or segments of paved surfaces, such as roads, sidewalks, or driveways, are raised or uplifted unevenly and has been displaced from its original position due to external factors.
What is Root Heave?
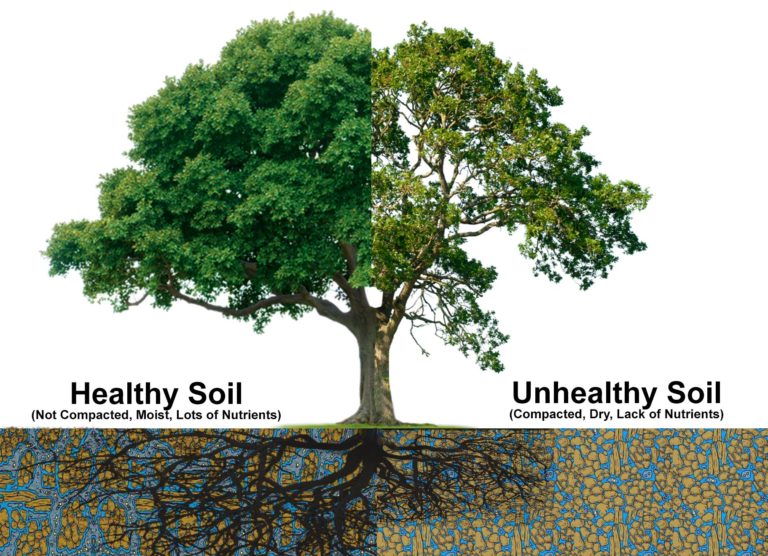
Root heave is a phenomenon where tree roots beneath the ground exert upward pressure as they search for nutrients, water and oxygen, causing pavements and urban infrastructure like sidewalks and driveways to lift and crack. This can lead to safety hazards and aesthetic issues, making it crucial to understand and address how to plant a tree to avoid root heave
How to Stop Root Heave?
Preventing root heave is far more effective and cheaper than dealing with it after the fact. By adopting the right strategies and planting techniques below, you can avoid the costly upheaval and damage caused by tree roots, ensuring the longevity of your pavement.
Ways to Prevent Tree Roots Causing Pavement Lift
Safeguarding your sidewalks from tree root damage requires a thoughtful proactive approach before the tree is even planted in the ground. Below we’ve detailed several methods that can be employed to prevent tree roots from undermining the stability of your pavement and urban infrastructure.
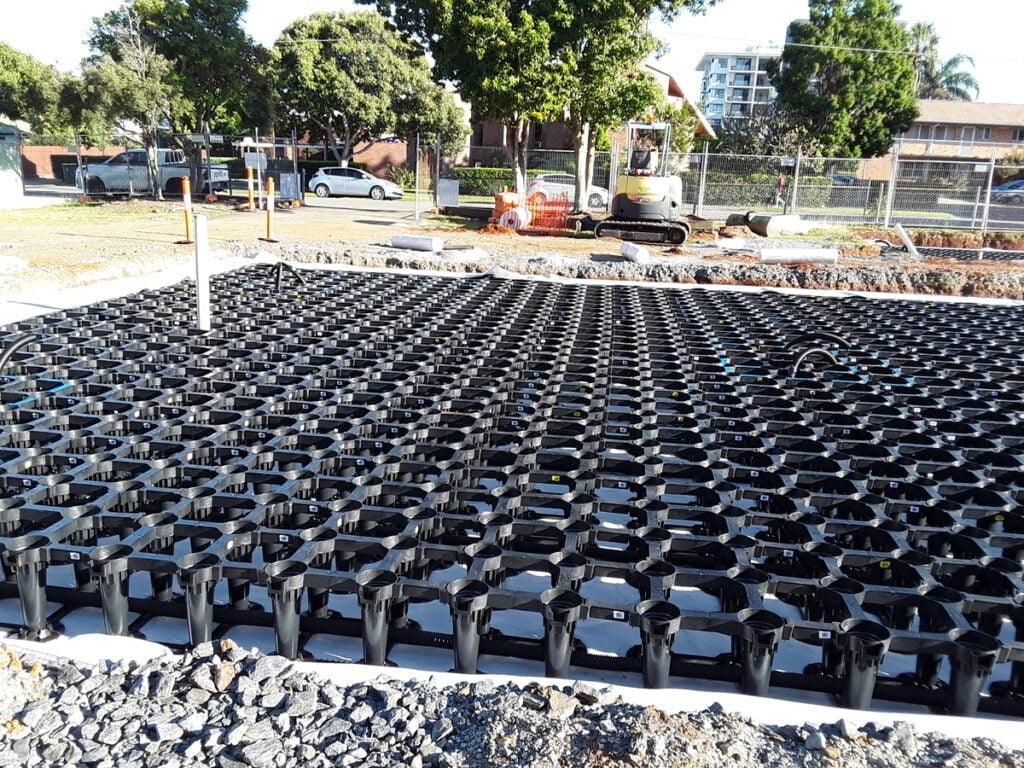
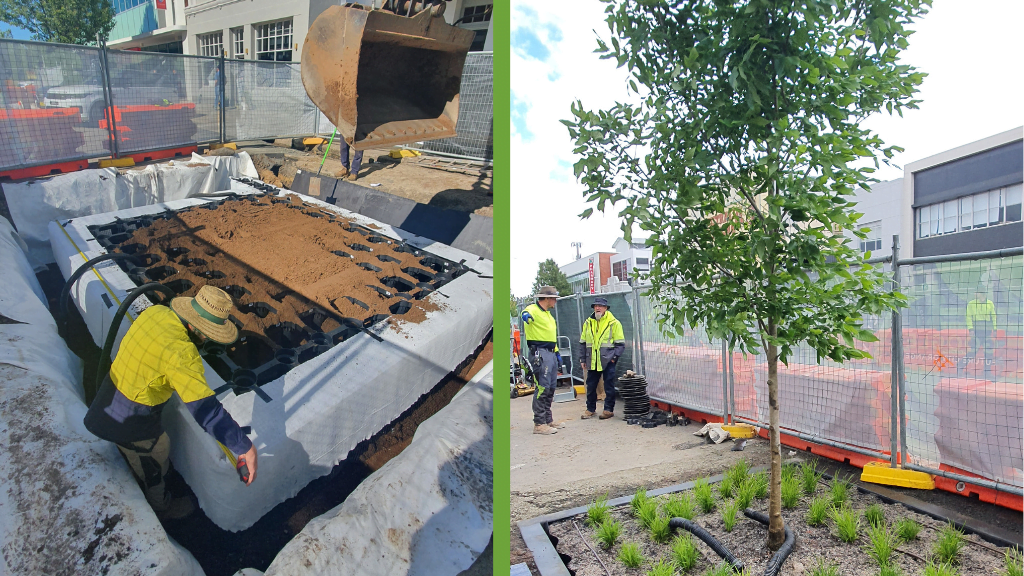
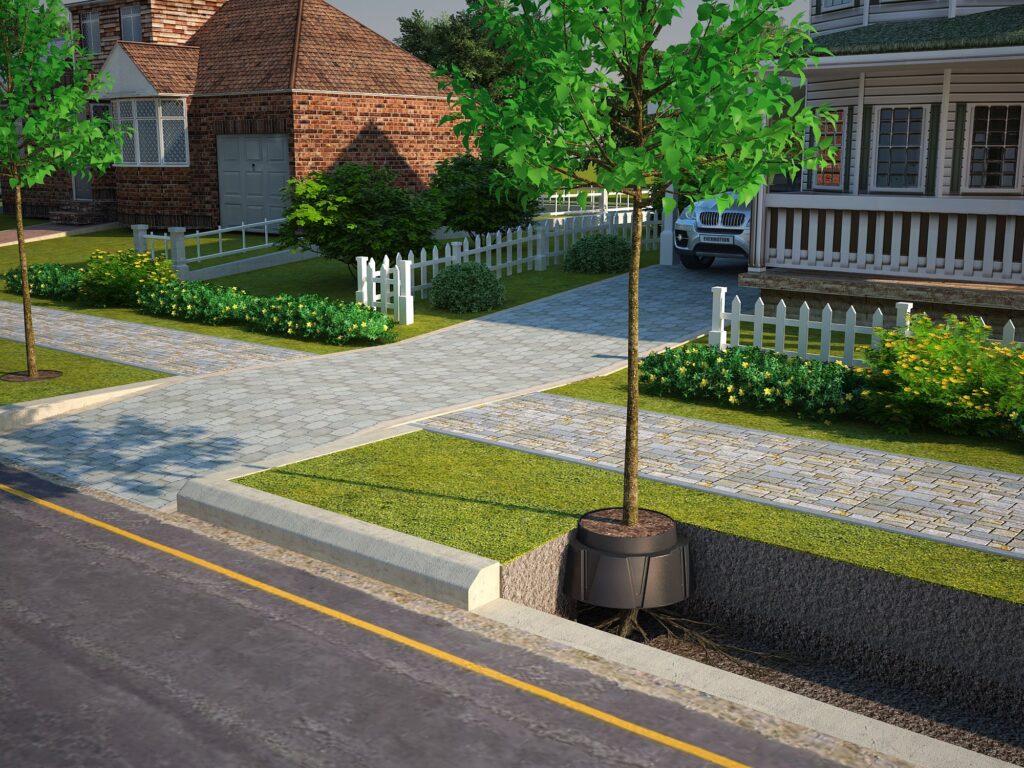
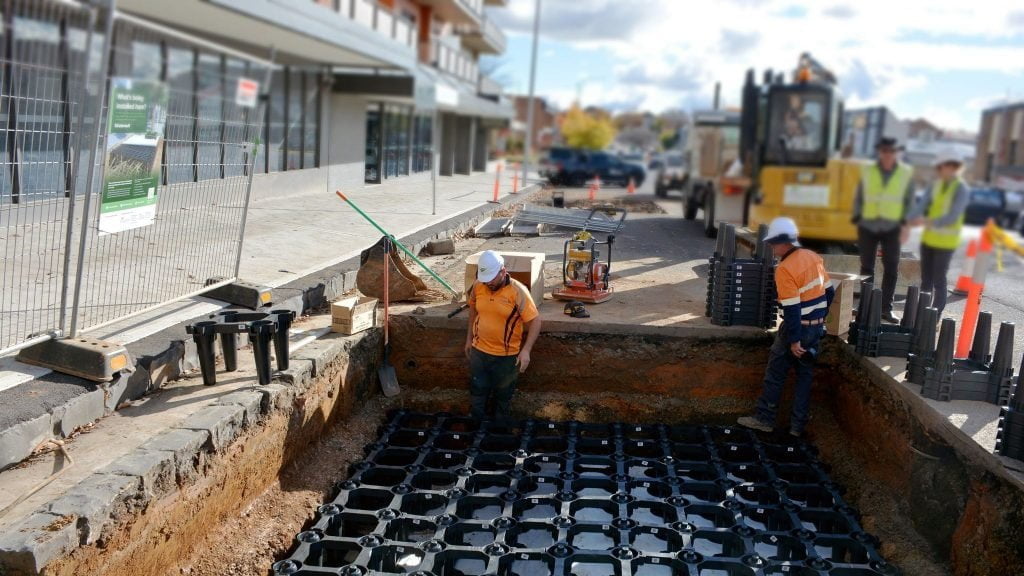
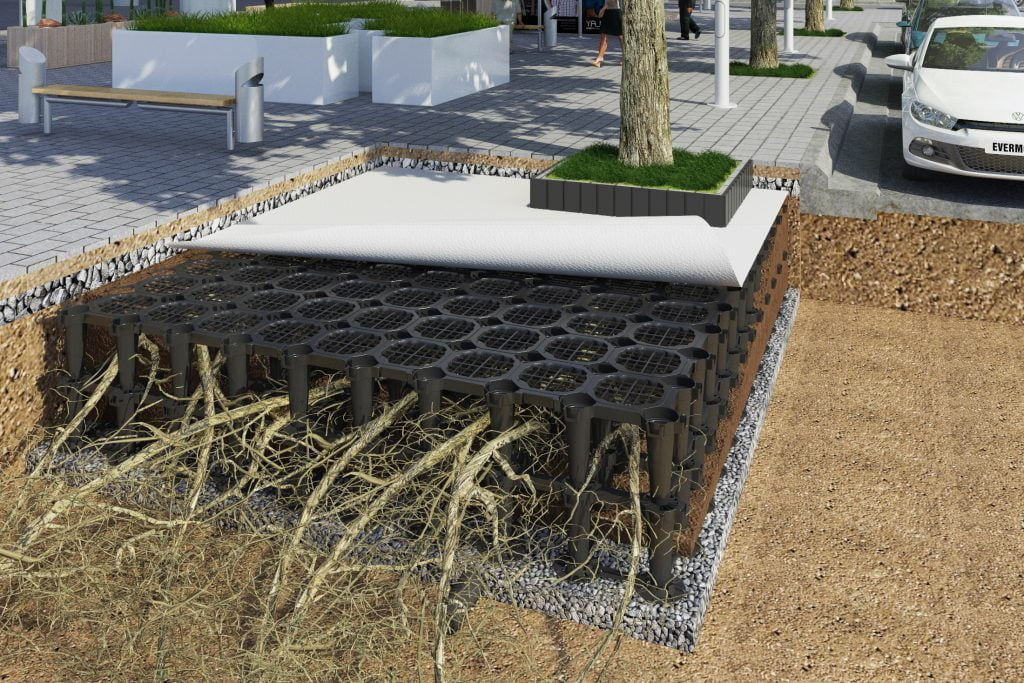
Use Soil Vault Systems

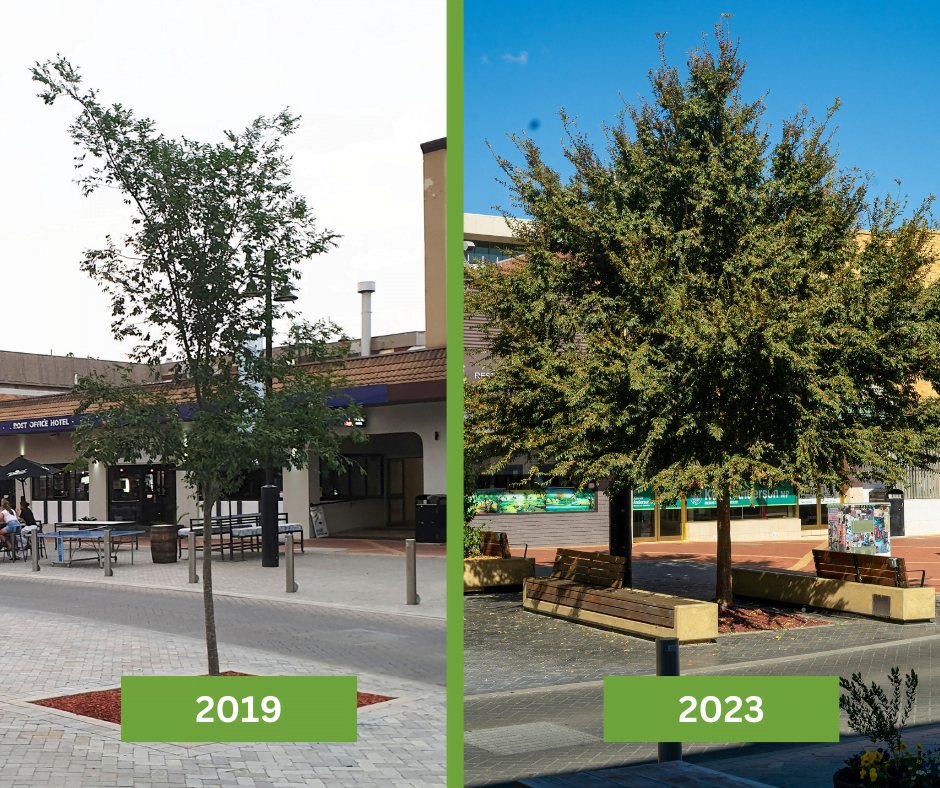
Using Soil vaults systems otherwise known as soil cells such as those developed by Citygreen allow tree roots to grow in ideal growing conditions while protecting surround infrastructure from tree root disturbances.
A top use case for soil vault systems is that it is rated for vehicle loads so it’s great for street pavements, carparks, and stormwater management.
Download the free Stratavault PDF Tech sheet to better understand how to use stratavault soil cells to stop pavement heave and grow better urban trees.

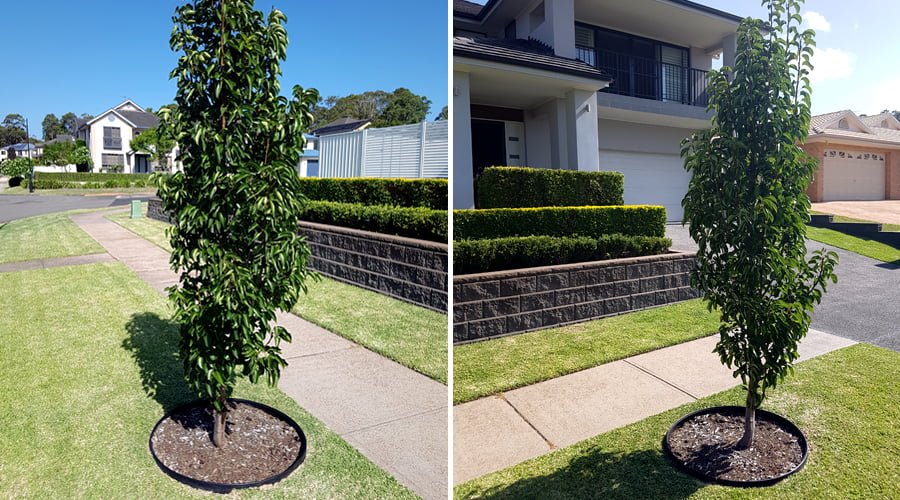
Proper Positioning of your Trees
Choosing the right location for tree planting is essential to prevent root-related problems. Proper positioning can minimize conflicts between tree roots and sidewalks, leading to a harmonious coexistence.
Properly positioning trees to avoid pavement lift and reduce conflicts with sidewalks and pavements is a critical step in urban tree management. Start by selecting tree species with non-invasive root systems, and consult with local experts for guidance. Reach out to your local government parks department or urban forester as they will be more then happy to send you a list of trees that are ideal for growing in your local climate.
Maintain a safe distance of at least five to ten feet between the tree base and nearby hardscape, allowing roots to develop without initially compromising pavement stability. Analyze soil conditions to ensure well-draining soil with adequate organic matter, which encourages healthy root growth away from pavements. We recommend using loamy soil but you can see our article on choosing the best soil for your tree here.
Plant trees at the right depth, avoiding shallow planting that may lead to horizontal root spread and deeper planting to promote root growth away from the surface. Regularly monitor root growth patterns and consider professional assistance to assess local conditions and choose suitable species and planting techniques. Well-structured tree pits with features like root barriers and proper drainage can direct root growth downwards away from infrastructure, ensuring a harmonious coexistence.
Related: How do Tree Roots Behave?
Bridging
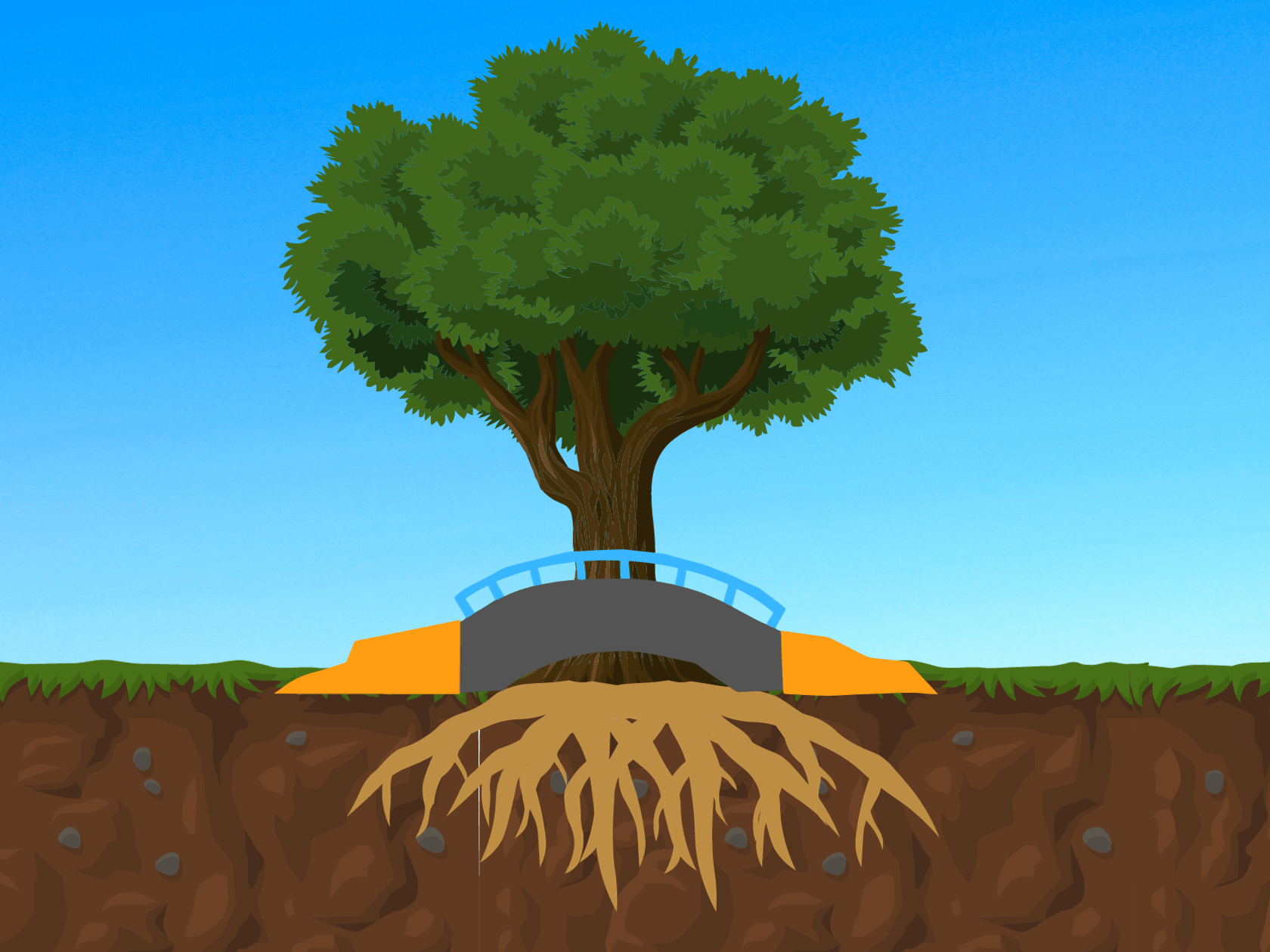
Bridging is a technique that creates a buffer zone between tree roots and pavements. This method involves installing materials that allow roots to grow beneath the sidewalk without causing upheaval. Creating a slope for your sidewalk involves the strategic use of posts, piers, or arch supports. These supports serve as the foundation for laying the sidewalk material, leaving deliberate space for the roots to grow beneath without causing disruptions.
One notable benefit of root bridging is its capacity to preserve existing tree roots, ensuring their continued health and enhancing overall stability. The choice of bridging materials can vary based on specific project requirements, including desired height, repair area length, and available budget. Commonly employed materials encompass wood, concrete, and composite materials.
However, it’s important to note that the design and construction of root bridging can be a relatively costly endeavor. In cases where the bridge elevation aligns with a typical step height (approximately 6 to 8 inches) relative to the surrounding grade, the installation of safety railings may be necessary. In certain scenarios, the incorporation of soil can be employed to seamlessly blend the bridge edge with the surrounding terrain, effectively eliminating any abrupt step-off points.
As root bridging can be expensive and incorporate alot of safety factors, it’s better to plan your tree planting to ensure that the trees roots have the best chance of growing deeper to never distrub the surface.
Root Barriers

Barriers such as Root Directors or Reroot Barriers are a great preventative measure designed to direct and guide exploring roots down and away from services and infrastructure. They are best installed when the tree is newly planted so when the roots expand and reach the barriers they will be directed deeper into the soil instead of staying in the upper levels of the soil.
Installing Snorkils also help greatly in enticing the tree roots to explore downwards to help avoid pavement lift as the Snorkil gives access to oxygen and water at a lower depth so the roots don’t have to keep near the surface to access the nutrients it needs to survive.
Reinforcing Collars
Similar to Root Barriers reinforcing sidewalks with concrete collars or gravel aggregate helps deter tree roots from growing beneath them, thus preventing damage and upheaval.
Additionally, adding a layer of compacted gravel or pebbles beneath the sidewalk can create a path for tree roots to follow, reducing the likelihood of pavement damage as tree roots prefer to grow in the path of least resistance.
e.g. Trees roots grow faster in uncompacted soil when compared to compacted soil due to the tree having to expend less energy to push through the soil in search of oxygen, nutrients, and water.
Tree Removal
In cases where tree roots pose an imminent threat to pavements, roads or infrastructure; where there is direct safety issues involved, tree removal or relocation may be a necessary but last resort option to prevent further damage.
What to Avoid When Dealing with Tree Roots
Understanding what not to do when dealing with tree roots is as crucial as knowing the right techniques. Certain actions can exacerbate the problem and lead to more significant damage.
For example, removing too much of a tree root could create a void space that can no longer support the above pavement which cause create further issues.
Tree Care Services Can Help Prevent Damage to Your Property
Professional tree care services can provide expert guidance and assistance in managing tree roots and preventing damage to your property. Their expertise can be invaluable in maintaining both your trees and pavements.
Tree Roots Pushing Up Driveway – What To Do
If tree roots are causing your driveway to heave and crack, specific actions can help address the issue, restoring the functionality and appearance of your driveway.
First Signs of Tree Root Damage
Recognizing the early signs of tree root damage is essential to address the issue promptly.
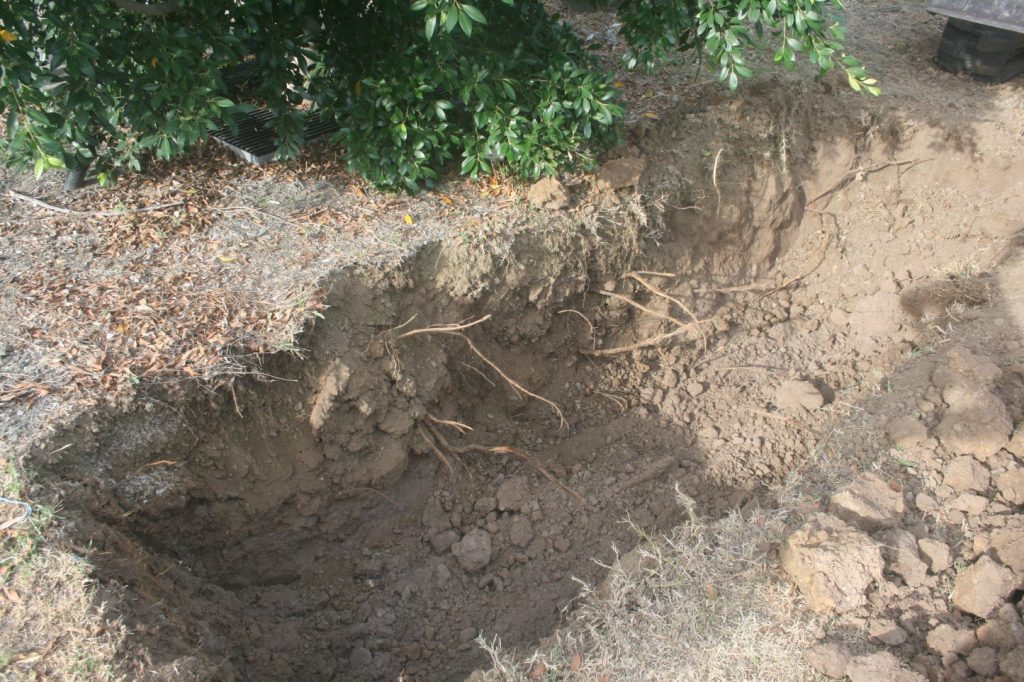
The initial signs of tree root damage to pavements and driveways can vary depending on the severity of the issue, but common early indicators include cracks, uneven surfaces, and pavement shifting.
The most noticeable sign of such damage is often cracking or sections of pavement lift that are uneven or lifted. These issues can pose trip hazards and make walking or driving difficult.
In some cases, instead of uplifting, the pavement may sink or settle due to soil erosion caused by root growth. As roots expand beneath the pavement, they can create an uneven surface or pockets of air below the pavement and make it challenging to walk or drive smoothly.
Advanced cases may even reveal visible tree roots breaking through the pavement surface or pushing it upwards. Additionally, the pressure from tree roots can not only damage the pavement but also lead to cracks in nearby structures like retaining walls, curbs, or foundations.
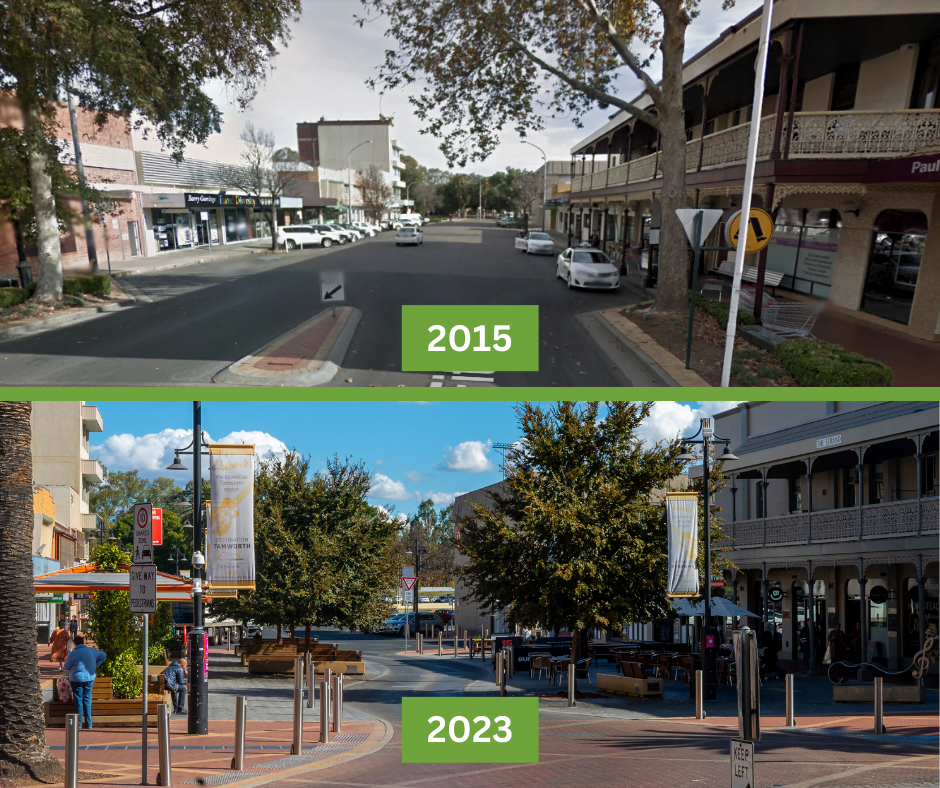
Plan Ahead to Avoid Tree Root Damage to Urban Infrastructure
Effective planning and design are key to avoiding tree root damage causing pavement lift. By taking precautions during the initial stages, you can prevent future issues.
At Citygreen, we are the industry leaders in designing urban landscapes that protect both the tree and the urban infrastructure. If you are looking to understand the range of tools you can employ to reduce tree root damage over the long term we recommend booking a 1-hour discovery call with our team.
Kill the Tree Root with Copper Sulfate
Copper sulfate, a cost-effective herbicide and algaecide, is commonly used to clear tree roots from sewer lines and pavements. However, before use, check local regulations due to its potential toxicity and environmental impact. Inspect your local area to assess the root infestation’s severity. Be cautious around pets, as it can be toxic to animals.
Test the sewer line by flushing the toilet, and repeat treatments if needed. Periodically flush copper sulfate to prevent new root invasions, and consult various references for further information on its use.
Remove the Root
Removing the offending tree root is a direct but sometimes necessary solution to eliminate damage and upheaval caused by tree roots. ensure the structural integrity of the tree isn’t compromised.
































