Posted by Sean Corrigan on Tue, Dec 05, 2023 @ 5:16 AM
Is Green Infrastructure Expensive?

Green Infrastructure is seen as expensive when compared to traditional grey infrastructure.
But with the increase of green infrastructure technology is this actually the case?
A study comparing the actual project costs to typical costs for conventional development found that 11 out of 12 diverse projects with direct cost comparisons between conventional and green infrastructure approaches showed cost decreases averaging 36%.
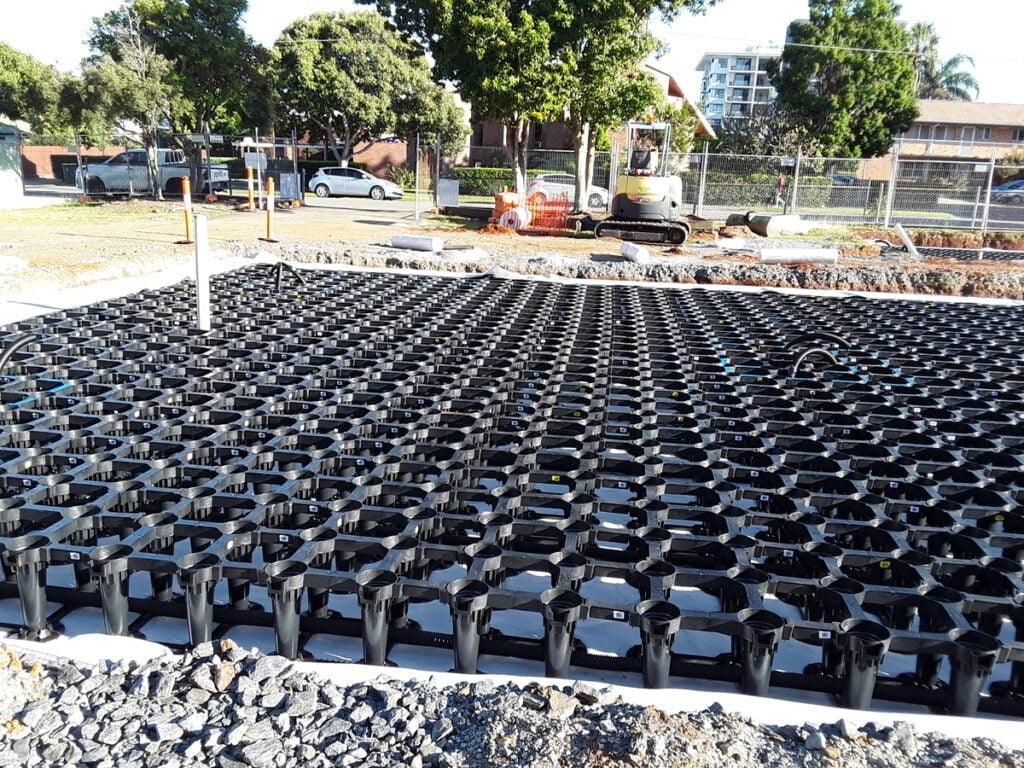
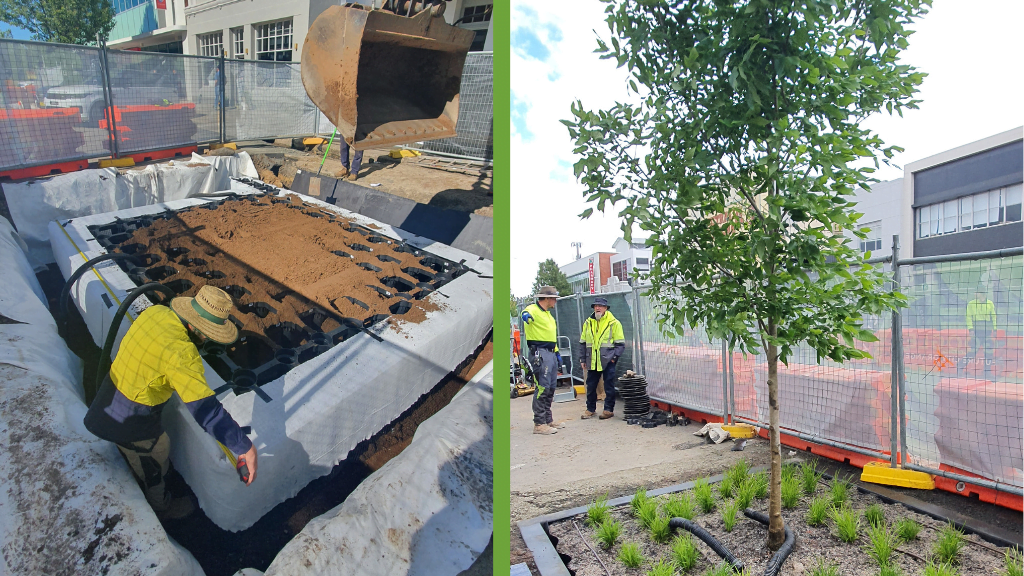
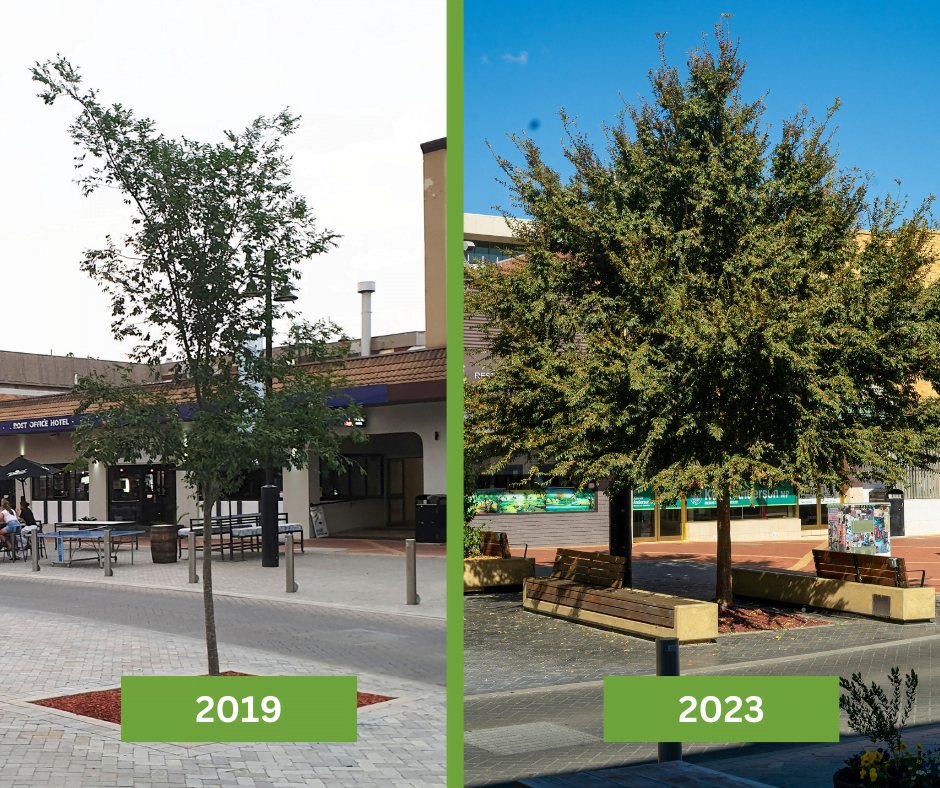
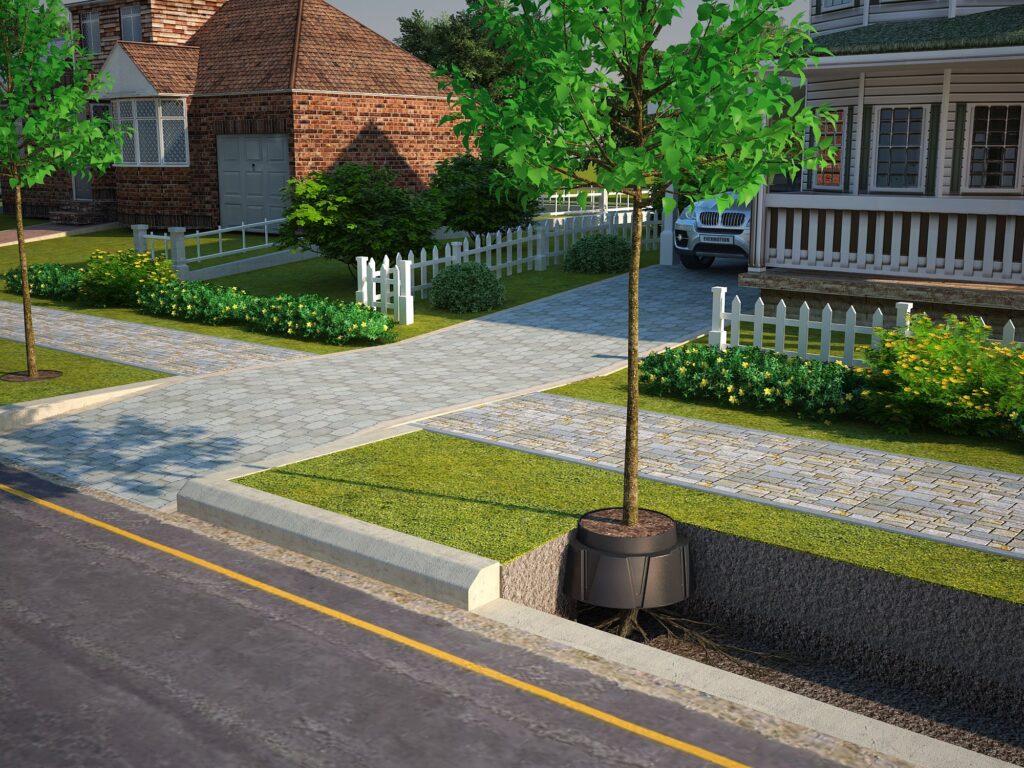
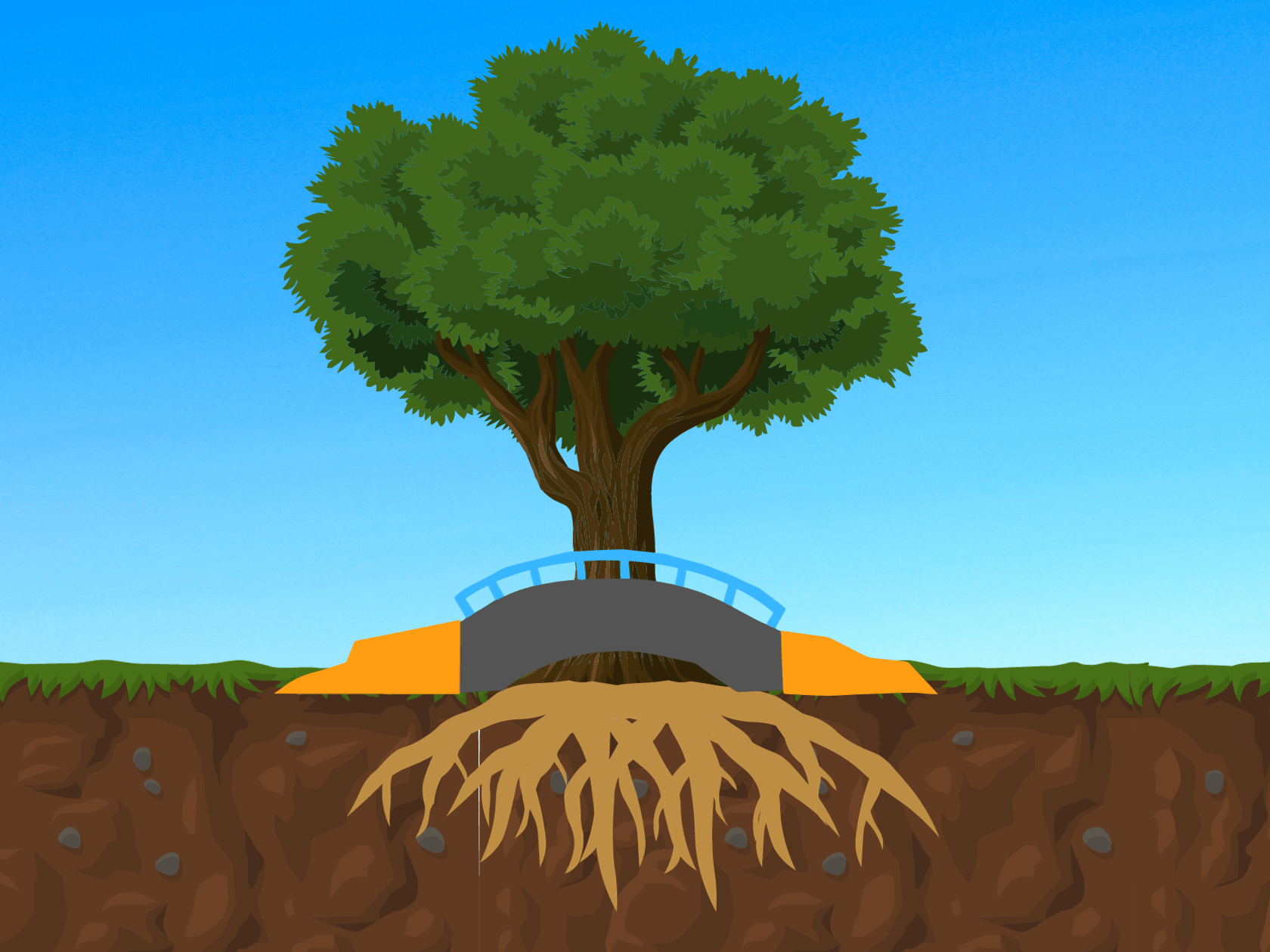
Green infrastructure, such as soil vaults and permeable pavement, can lower water treatment costs, reduce flooding, and erosion, thus providing economic and environmental benefits to the city.
What are the Typical Costs of Green Infrastructure Projects?

The cost of green infrastructure can be influenced by factors such as the type of project, location, and integration with planned infrastructure improvements.
Integrating green projects with planned infrastructure improvements, such as road reconstruction or roof replacements, can lead to cost savings of 30% to 60% over the lifetime of the project due to the multiple benefits that green infrastructure offers back to the built environment.
It is important to note that the cost of green infrastructure is not solely determined by the initial construction costs but also includes life cycle costs, including planning, design, installation, operation and maintenance, and replacement.
The cost-analysis of green infrastructure should be analyzed in conjunction with its performance and the multiple benefits it provides, including environmental, economic, and community benefits.
How do Cities Fund Green Infrastructure Projects?

Cities typically fund green infrastructure projects through a variety of mechanisms, including public and private sources. Some of the common funding sources and mechanisms highlighted in the search results include:
- Public Sector Financing: Cities can use their main revenue sources, such as property taxes, transport fees, and other charges, to finance green infrastructure projects. They can also explore the greening of municipal financial instruments, such as congestion charges, variable parking fees, toll lanes, and split-rate property taxes, to achieve greener urban infrastructure1.
- Private Sector Involvement: Public-private partnerships (PPPs) are a common mechanism for involving the private sector in funding green infrastructure projects. In PPPs, the long-term risk is transferred to the public sector, and they can play a significant role in financing and implementing green infrastructure projects1.
- Grant Funding: Grant funding, including federal grants, can provide local governments with the resources to implement green infrastructure projects. However, federal grants can be highly competitive2.
- Federal Programs: Federal programs that support efforts to reduce water pollution and manage stormwater can provide funding for green infrastructure projects. For example, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) provides funding for such projects.
- Community Development Funds: Community development money can be used to fund green infrastructure projects because these projects can create jobs, increase economic activity, and increase property values. Urban tree planting and green infrastructure can increase economic activity in a commercial district and property values by mitigating flooding and improving neighborhood aesthetics3.
- Transportation Funding: Green infrastructure projects are often eligible for transportation funding because they improve transportation networks by efficiently and cost-effectively mitigating street and alley flooding and create a cooler more comfortable environment for passengers.
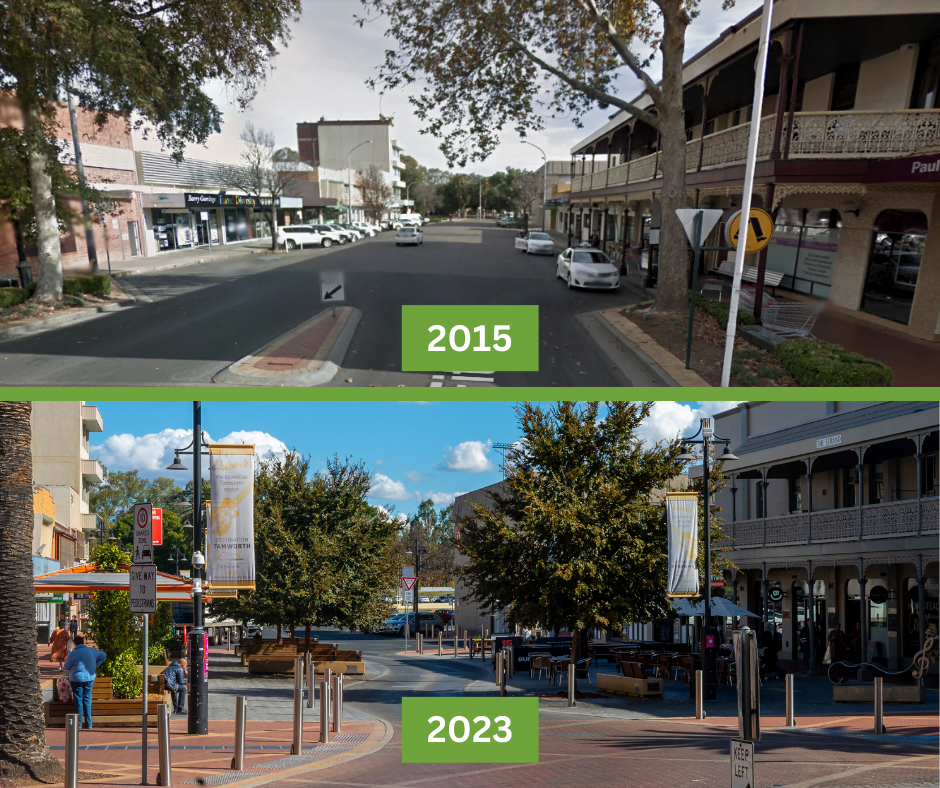
A great way to ensure green infrastructure gets built is to set it as a building standard for new constructions and incorporate GI into street layouts and designs.
Citygreen regularly works with local and state governments worldwide to improve their city standards towards tree canopy and green infrastructure. Our team can advise you on actionable goals and solutions to cool your city with green solutions.
How To Do Green Infrastructure Cost Analysis?

To conduct a green infrastructure cost analysis, the following steps can be taken:
- Define Green Infrastructure and Public Space: Green infrastructure is the network of green spaces, natural systems, and semi-natural systems that support sustainable communities, while public spaces are places publicly owned or for public use, accessible and enjoyable by all free and without a profit motive.
- Cost Benefit Analysis: Measure incremental change relative to what would have happened without action, i.e., the base case. The CBA should only consider the incremental or marginal impact of a program or project. Specify the base case in as much detail as possible and quantify it to set a baseline for the incremental changes in outcomes that are being measured. including identifying the developing options, identifying and forecasting costs and benefits, valuing costs and benefits, identifying non-market impacts, and reporting the results of CBA.
- Consider the Costs of Green Infrastructure and Public Space: The costs of such projects include construction costs, costs related to the replacement of capital, and costs related to ongoing maintenance and operation. Cost estimates should be specific to the individual project and reflect the design and conditions associated with the construction and operation of the project.
- Value the Benefits of Green Infrastructure and Public Space: The benefits of public space are driven by a range of features, and the framework provides recommended approaches and parameters for valuing these benefits. It’s important to carefully consider the specific benefits associated with the project and apply the recommended parameters accordingly.
- Engage with Stakeholders: In addition to using the framework, practitioners should engage with stakeholders, including the department’s subject matter experts and the community to understand the full use case of the infrastructure.
By following these steps, practitioners can conduct a comprehensive green infrastructure cost analysis that takes into account the economic, social, environmental, and cultural costs and benefits of the project.
Our team is well versed in the world of Green Infrastructure and stormwater management and can provide you with a free quote for your next project.
What are the Benefits of Green Infrastructure?

There are a multitude of benefits related to green infrastructure that cities that consistently invest in green infrastructure are seeing.
Energy Efficiency
Green Infrastructure reduces the cooling demands of households, and buildings through creating shade and transpiration of water through leaves from trees and plants. The NSW government estimates that for each reduction in degree through tree canopy you decrease your energy bill by $13.
Air Quality Improvement
Increasing tree canopy and urban green walls contribute to air quality improvement through capturing of physical and gaseous pollutants, suspending captured particles, emitting environmentally friendly particles like pollen, and disrupting of wind flows through tree canopy.
Water Management
Green Infrastructure can capture water runoff, which reduces the volume of stormwater that needs to be processed and be used to sustain the green infrastructure itself. It additionally improves the water quality of runoff that does reach the waterways.
In the ‘Valuing green infrastructure and public spaces Framework’ from the NSW Government. The estimate the value of stormwater reduction based on the avoided costs of projects to build additional stormwater management infrastructure like wetlands and retention ponds.
Some key data points from that analysis:
- Cost to manage stormwater flows ranged between $0.04 to $0.30 per cubic metre captured, depending on the type of infrastructure option
- An average-sized street tree in Canberra captures 16,500 L (16.5 cubic metres) annually
- A hectare of irrigated urban forest would capture 1 megalitre (1,000 cubic metres) of stormwater per 20 mm rain event
So in summary, the document states green infrastructure and trees can reduce stormwater runoff, avoiding the need for additional “grey” stormwater infrastructure. This avoided expenditure provided an approach to quantifying the stormwater management benefits.
Health Benefits
Green Infrastructure has far ranging impacts in the areas of mental and physical health. Increasing the amount of green infrastructure in the forms of public open spaces, parks, and facilities shows a 6% increase of residence hitting their daily activity goal which equals around a $1.13 cost saving per household per km walked.
Urban cooling through tree canopy and transpiration also reduces heat-related health complications. The NSW Government estimates 1°C of cooling saves $3 per person per very hot day in health costs and an 10% increase in canopy cover is equal to a 1.1°C cooling effect.
We invited General Practitioner Dr. Kim Loo to come speak at our event ‘Where Shade hits the Pavement’ to discuss how trees and urban planning are impacting her patients in Western Sydney.
Takeaway
Despite its complexity, the wide-ranging benefits of green infrastructure unfold gradually over time. While there exists an initial upfront cost during the construction phase, this investment quickly shows substantial returns, growth and impact for the community.
As the effects begin to manifest in the economic, social, and environmental spheres, the return on investment becomes increasingly evident. The transformative power of green infrastructure becomes apparent when measuring its positive influence on economic savings, social well-being, and environmental sustainability.
Therefore, while the initial costs might seem substantial, the long-term advantages and dividends gained from the implementation of green infrastructure undoubtedly outweigh these initial expenses, making it a wise and forward-thinking investment for communities and regions alike.