Posted by admin on Thu, Jul 16, 2015 @ 1:02 AM
Tree Root Management in Urban Areas

While we need trees within our cities – to provide shade, reduce the heat-island effect, clean the air and house wildlife – managing tree roots from interfering with infrastructure is an on-going issue. The most effective solution is to direct them away from surrounding infrastructure and services.
An understanding of how tree root management is important in addressing this problem. The key points in managing tree roots are these:
- Roots have two main roles –anchoring street trees in the ground and collecting minerals, oxygen and moisture to supply the tree. They are also a store of moisture and nutrients.
- The root cap is a mass of cells at the tip of the root. It grows by lengthening cells behind the root cap, forcing the root tip through the soil.
- Minute root hairs sprout behind the growing tip and absorb soil moisture.
- Roots grow where water, minerals and oxygen are found in the soil which is usually in the surface layer of soil. Hence the largest concentration of feeder roots exists in this zone.
- Tree roots can be guided to grow in certain directions to avoid disrupting surrounding infrastructure, with minimal impact on the tree.
- A trees roots must be pruned at the edge of the root ball prior to final installation. This helps insure correct regrowth of the roots outwards and helps negate root swirl.
- Species selection is crucial. Discuss the significance of selecting suitable tree species for urban environments, considering factors like growth patterns, root systems, and compatibility with surrounding infrastructure. Using a Soil Vault system can help enable large mature canopy trees in complex urban environments.
Related: Top Products for Tree Root Management
Root Barriers for Tree Root Management
Root barriers are typically used to guide them away from infrastructure and can also protect pavements, footings and kerbs from cracking and lifting. Usually made from either virgin or recycled industrial polymers, root barriers come in various forms and sizes. These include the ribbed modular units, the ribbed linear material and also the dimpled and non-ribbed linear material. Continuous lengths of material are available in a range of widths that can be installed to various depths depending on the application. Citygreen supplies linear ribbed barrier in 300mm deep rolls for applications tree roots only need to be deflected fairly superficially such as to protect a standard pedestrian kerb line from surface rooting. Depths of 600mm and 1000mm are also available for the protection of paved surfaces, shallow service ducts and utilities, while a high strength 2000mm deep root barrier has been developed for deeper applications. For example, this width is often used in new service infrastructure projects, business parks and housing developments.
Root barriers are best laid before the tree is established although often root barriers for mature trees can be retrofitted around existing trees. The barrier is able to curve around obstacles and is often rigid enough to hold its form when backfilling. It also protects the tree when pavement reinstatement works are carried out.
Preformed, ribbed modular units, or Root Directors, are also available and incorporate many critical features such as tapered sides, prominent root training ribs, no joins for root penetration and ground locking panels to resist root heave. These units may be used to protect pavements and hard landscaped areas, diverting root growth downward and outward. Installers report that these units are simple and quick to install, however designers and contractors must ensure that an appropriate model is selected, relative to the mature size of the tree species.
Finally root barriers may be laid horizontally over the root zone of newly planted street trees to prevent the roots growing laterally under the pavement.
Overall barriers are beneficial for trees. Roots are protected, a deeper system is encouraged and the tree gains greater drought tolerance and improved stability.
Structural Soil Cells for Tree Root Management
Citygreen, an industry leader in sustainable urban solutions, offers the Stratavault system, structural soil cells designed to house tree roots in urban environments while providing a structural base for pavements, roads and other infrastructure projects. The soil cell otherwise known as soil vaults are ideal for applications where tree roots need to be contained to avoid tree root heave for safety concerns, such as protecting standard pedestrian kerb lines from tree roots surfacing and cracking the road, kerb and pavement.

Using soil cells has also been shown to accelerate the growth of trees in urban environments due to the high level of soil that can be placed in the pit. The soil can then also be engineered to be tree specific also improving the growth rate of the trees.
Soil vaults such as Stratavault and Stratacell are designed with reducing the compaction strain on the soil and tree roots by dispersing the load through the matrix.
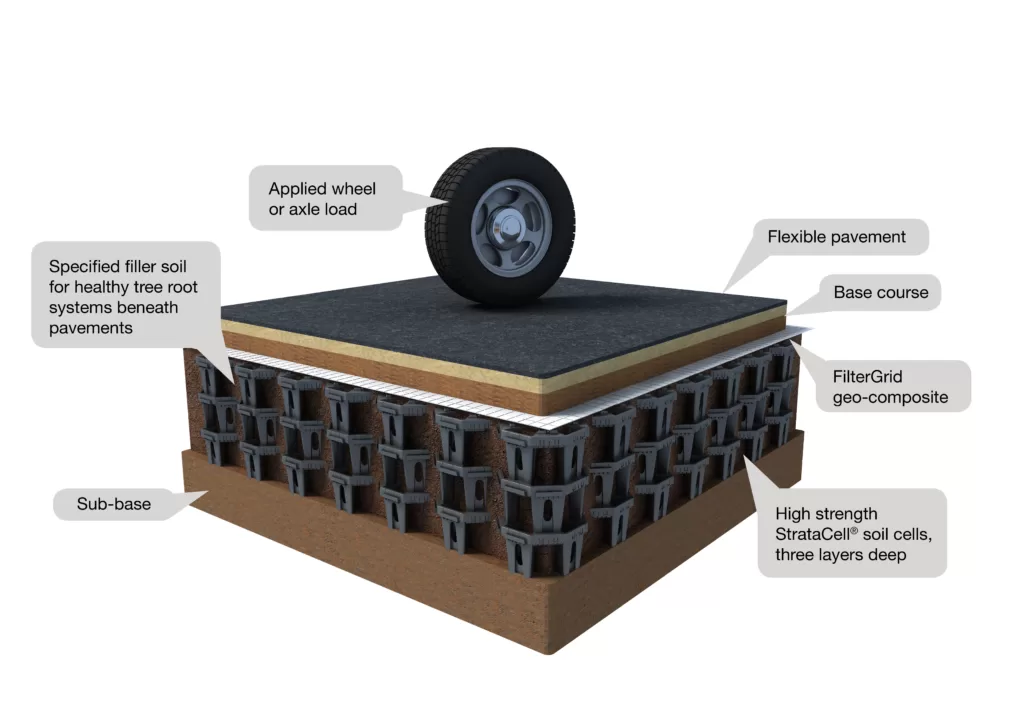
In standard urban plantings, trees are planted in higher compacted soil due to the need for load capacity of urban infrastructure which restricts the growth rate of trees as tree roots struggle to push through the hard compacted soil in search of water, nutrients, and oxygen.

